- What is a VPS?
What is a VPS? A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a way to partition a physical server into multiple virtual servers. Each VPS has the appearance and capabilities of a dedicated server, with full hardware emulation down to the BIOS level. Each Virtual Server is being allotted a specific amount of resources: Memory, Storage, and CPU. These resources can be scaled up or down, on demand. Each Virtual Server can run its own operating system, 32 or 64-bit, and each machine can be independently rebooted. All Virtual Servers are operating in complete isolation from each other.
- Console Access
Login name and password along with the access URL will be issued by CIFNet's Support Team once you sign up for the service. To gain access to your Virtual Private Server's console, you need to first log into the system using your web browser (Figure 1). If you're using IE or FireFox, you'll be required to add URL's SSL certificate as an exception.
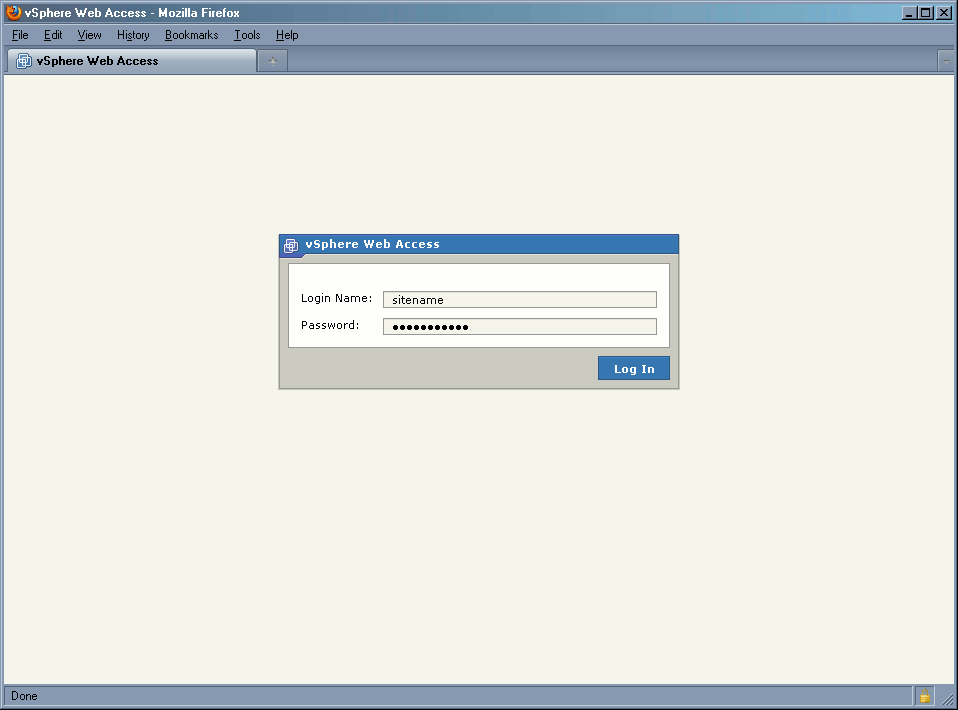
Figure 1.
Additionally, you'll be required to download and install "VMware Remote Console Plug-in". Once installed, your browser may need to restart to operate properly. Please review Figure 2 for more information.
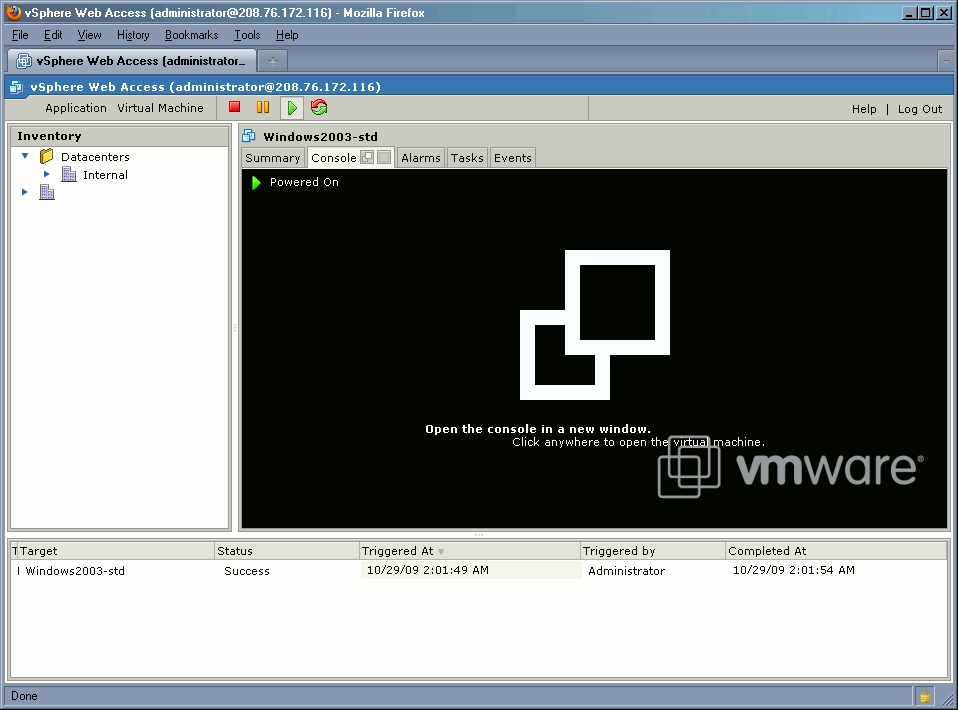
Figure 2.
A new console sreeen will appear as indicated just below this message
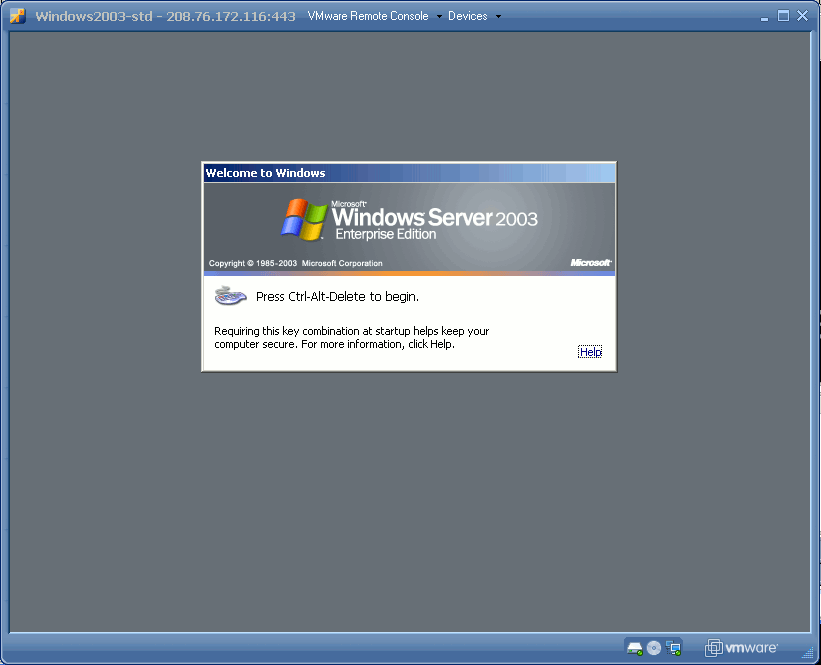
Figure 3.
To return control back to your desktop's computer, use Ctrl+Alt keys combination.
Please do not adjust interface speed and/or duplex settings. These are already preconfigured and changing them will not improve performance in any way.
- Data Transfer and Bandwidth
Data transfer is the total amount of information uploaded to and downloaded from your VPS. Whenever a visitor comes to your web site, data is being sent to your visitor's computer. This data may include web pages, images, videos, software packages, or compressed files — anything on your site that can be viewed or downloaded. The more visitors you have, and the more complex your web site, the more data transfer you'll use.
Although people often use these terms interchangeably, there is a significant difference. Data transfer is all of the information transferred from your system to end destination; bandwidth is the capacity of the link.
You can visualize data transfer as the number of cars on a highway, and bandwidth the number of lanes. While bandwidth remains fixed, your data transfer may change, depending on how many visitors your web site has.
We collect NetFlow information and aggregate that information into daily reports which can be seen at our portal. We do not count data within our network (AS14585 / CIFNet) toward your monthly Data Transfer. This means that the data transfered from one VPS to another will be free of charge, however, should you abuse it, we do reserve the right to change this policy.
- What Operating Systems are supported?
- Various Microsoft Windows products including Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit), Windows 2003 Web and Standard Editions, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7
- Multiple Linux Distributions (32-bit and 64-bit)
- FreeBSD (32-bit and 64-bit)
- A number of Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) series of Unix variants.
full list of officially supported guest operating systems can be found by following this link.
- Issue: Debian 5.0.3 w/ 2.6.26-2-686 kernel -- ifconfig shows incorrect data throughput. Steps to fix this issue are:
- edit /etc/apt/sources.list
- add "deb http://www.backports.org/debian lenny-backports main contrib non-free"
- aptitude install open-vm-tools
- then follow steps as described in the "/usr/share/doc/open-vm-source/README.Debian" document:
- module-assistant prepare open-vm
- module-assistant auto-install open-vm
- /etc/init.d/open-vm-tools restart
- Issue: Certain guest Operating Systems may have issues with time drifting away. We suggest setting up NTP to update time every hour or so. We also recommend reviewing the following url.